VAV1 Degrader Program: <font>In Vitro</font> and <font>In Vivo</font> Validation Data
Release time:
2025-06-26
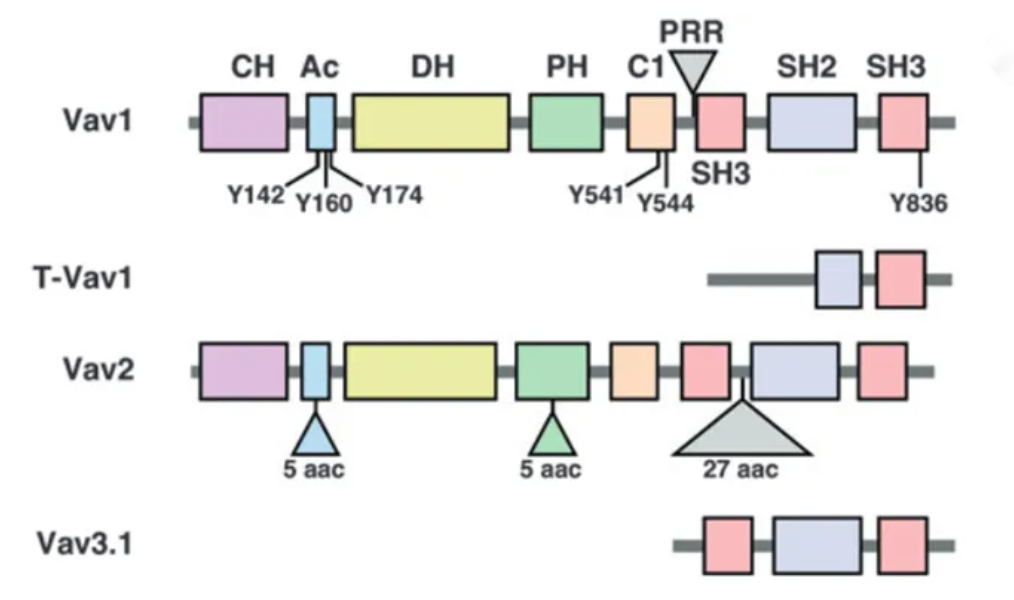
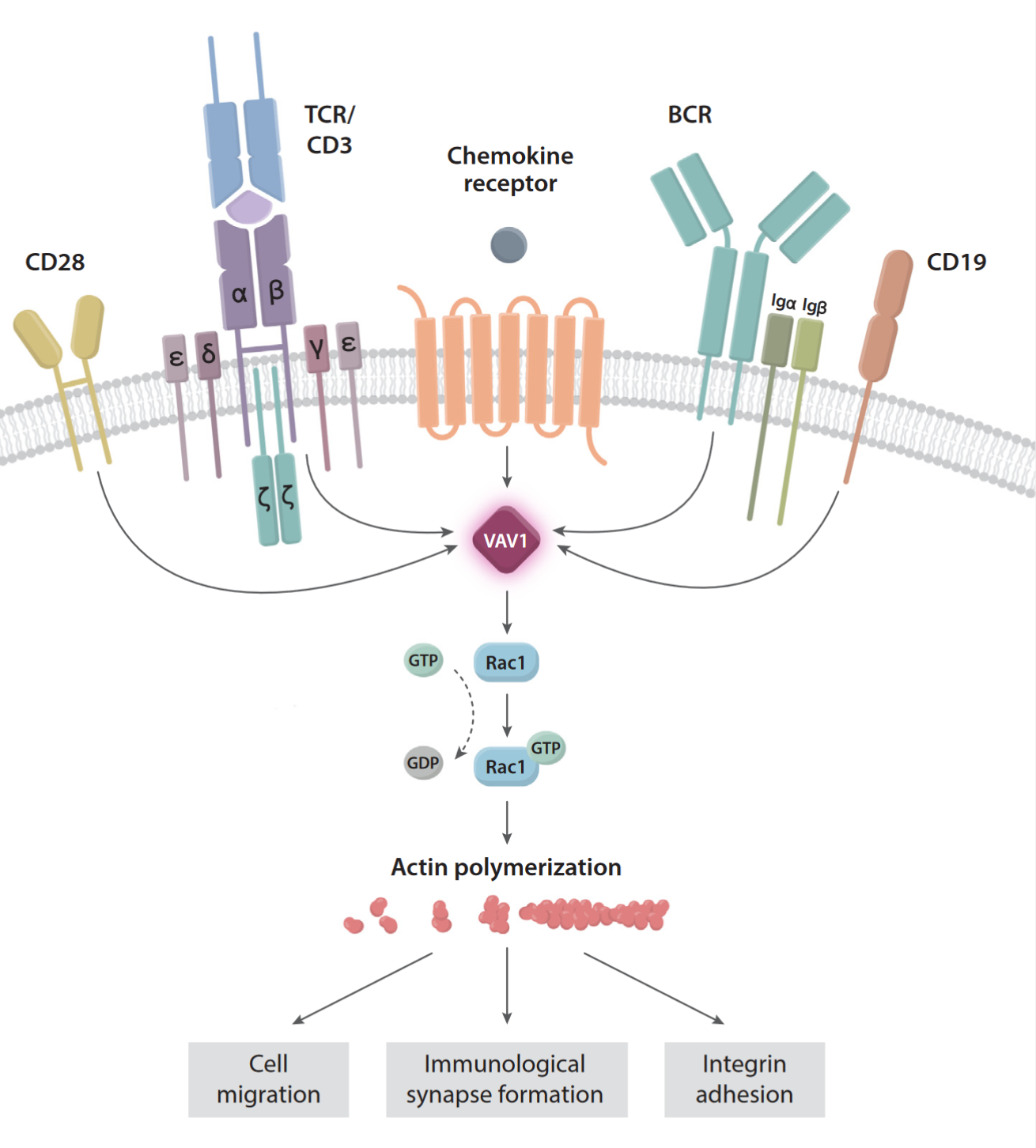
VAV1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for Rho family GTPases.
Introduction: Understanding VAV1
- VAV1 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for Rho family GTPases.
- It is primarily expressed in hematopoietic stem cells, including T cells, B cells, monocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells.
- VAV1 plays a key role in the function of immune cells, cytoskeleton reorganization, cell migration, proliferation, and cancer progression.
- Its core function is to regulate processes like cell migration and proliferation by activating Rho family GTPases.
- Aberrant expression or dysfunction of VAV1 is closely related to immune diseases and cancer, making it a significant research target.
VAV1 Degradation in 293T-VAV1-HiBiT Stable Cell Line
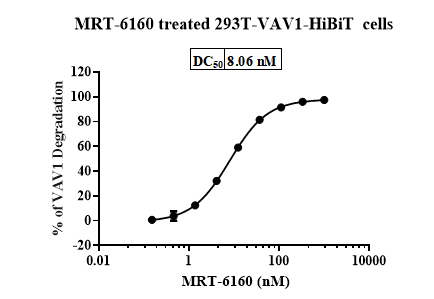
- Result: In 293T-VAV1-HiBiT cells, MRT-6160 degraded VAV1 with a DC50 of 8.06 nM and a maximum degradation (DCmax) of up to 98%.
- Application: This stable cell line can be used for high-throughput screening of VAV1 molecular glues.
VAV1 Degradation in Jurkat Cells
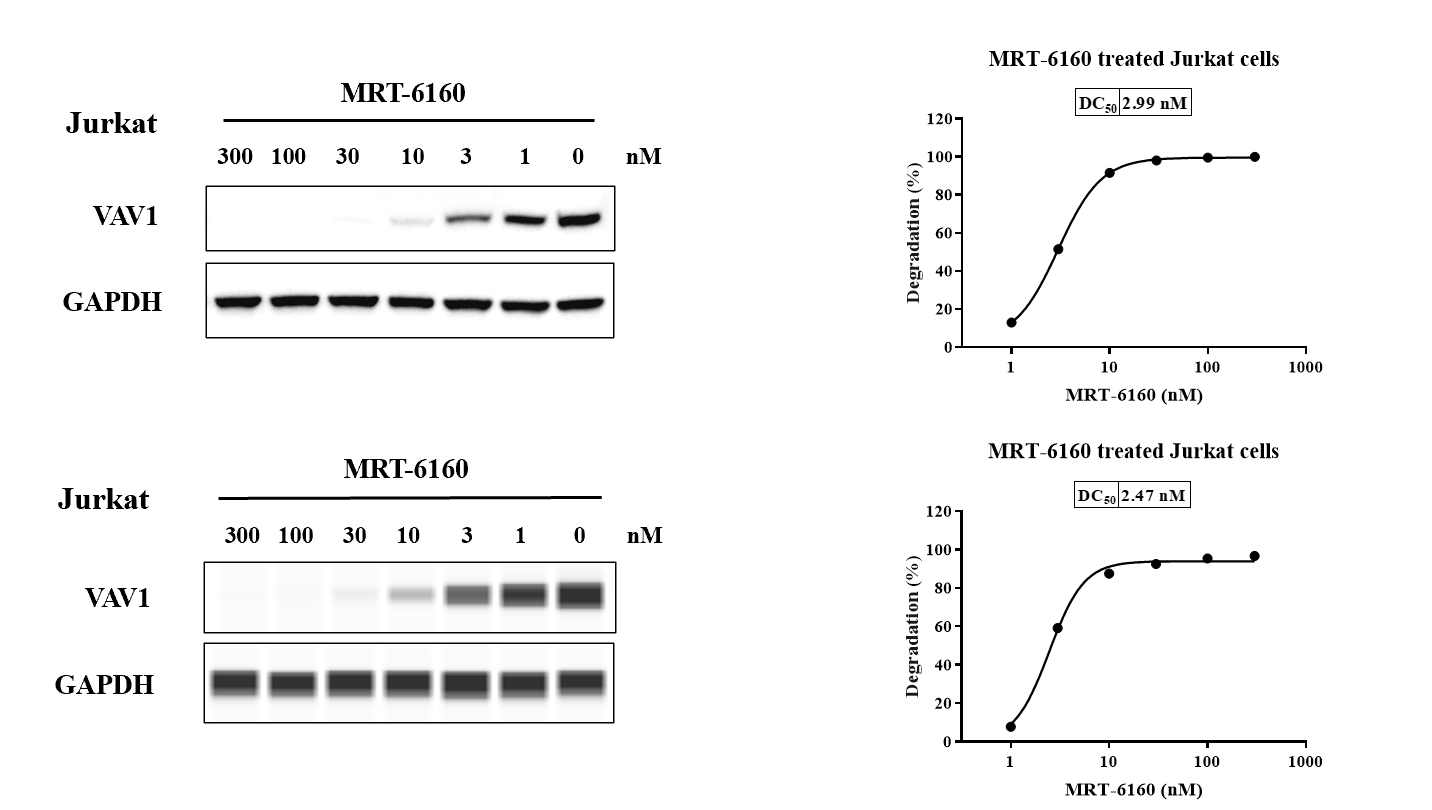
- Result: In Jurkat cells, MRT-6160 degraded the VAV1 protein with DC50 values of 2.99 nM (Western Blot method) and 2.47 nM (Abby method).
- Western Blot: The slide includes Western blot images showing VAV1 and GAPDH levels in Jurkat cells at various concentrations of MRT-6160.
VAV1-CRBN/DDB1 Binding Assay
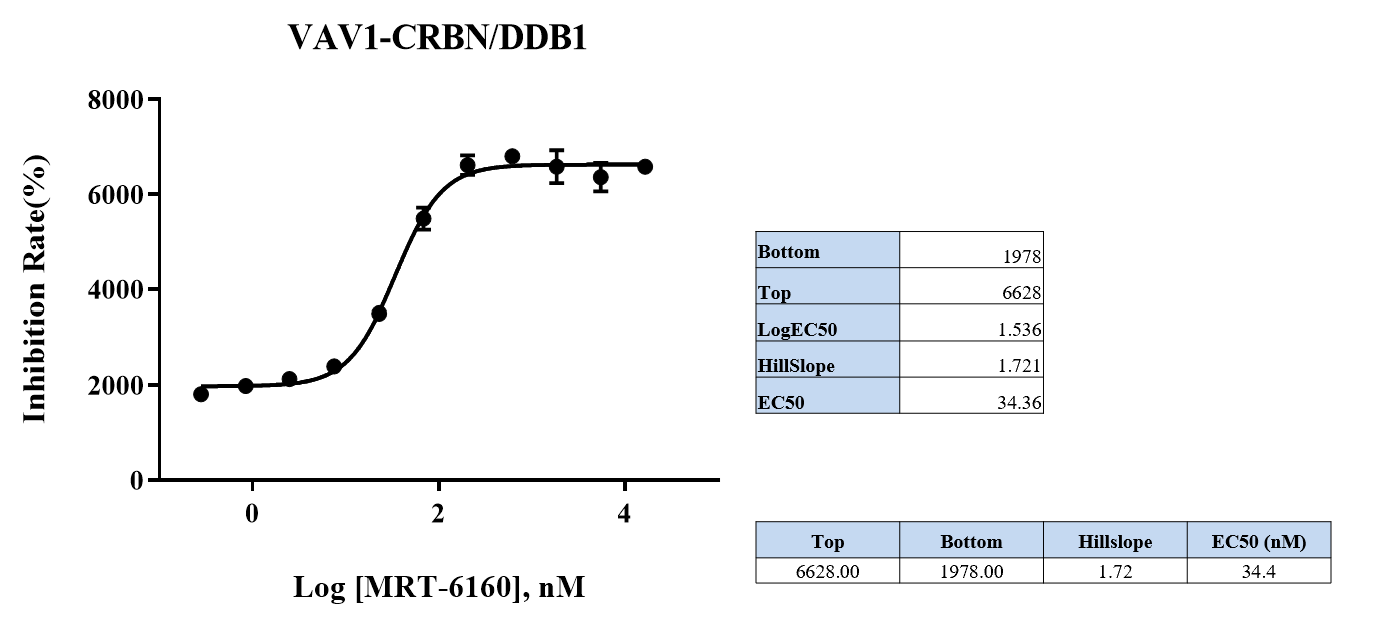
- Method: An AlphaLISA assay was used to detect that the degrader promotes ternary complex formation.
- Result: The EC50 for promoting complex formation was 34.36 nM. Other values include a HillSlope of 1.721 and a Top value of 6628.
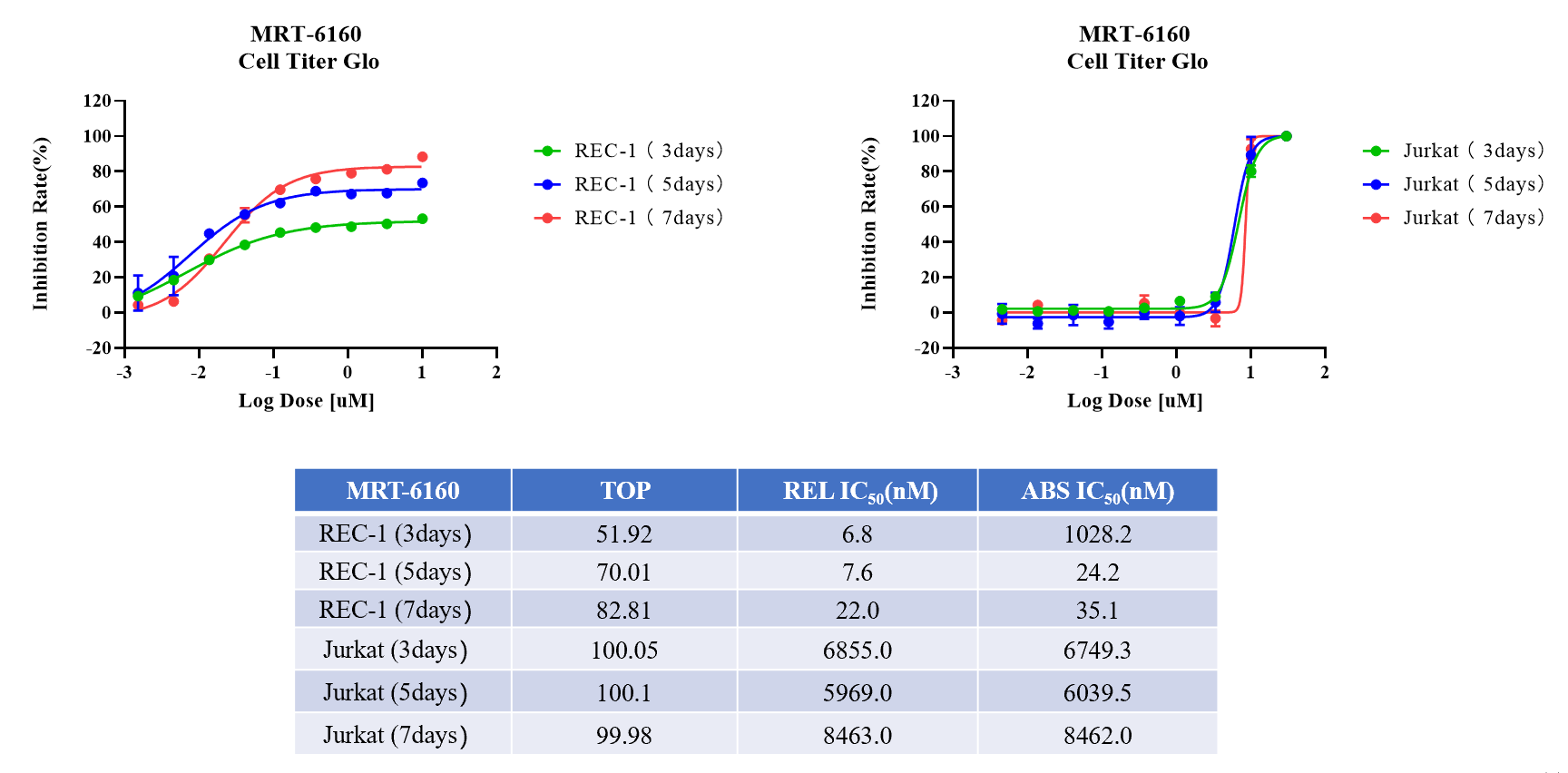
MRT-6160 Activity Test in Rec-1 and Jurkat Cells
MRT-6160 Biological Activity Test in T Cells
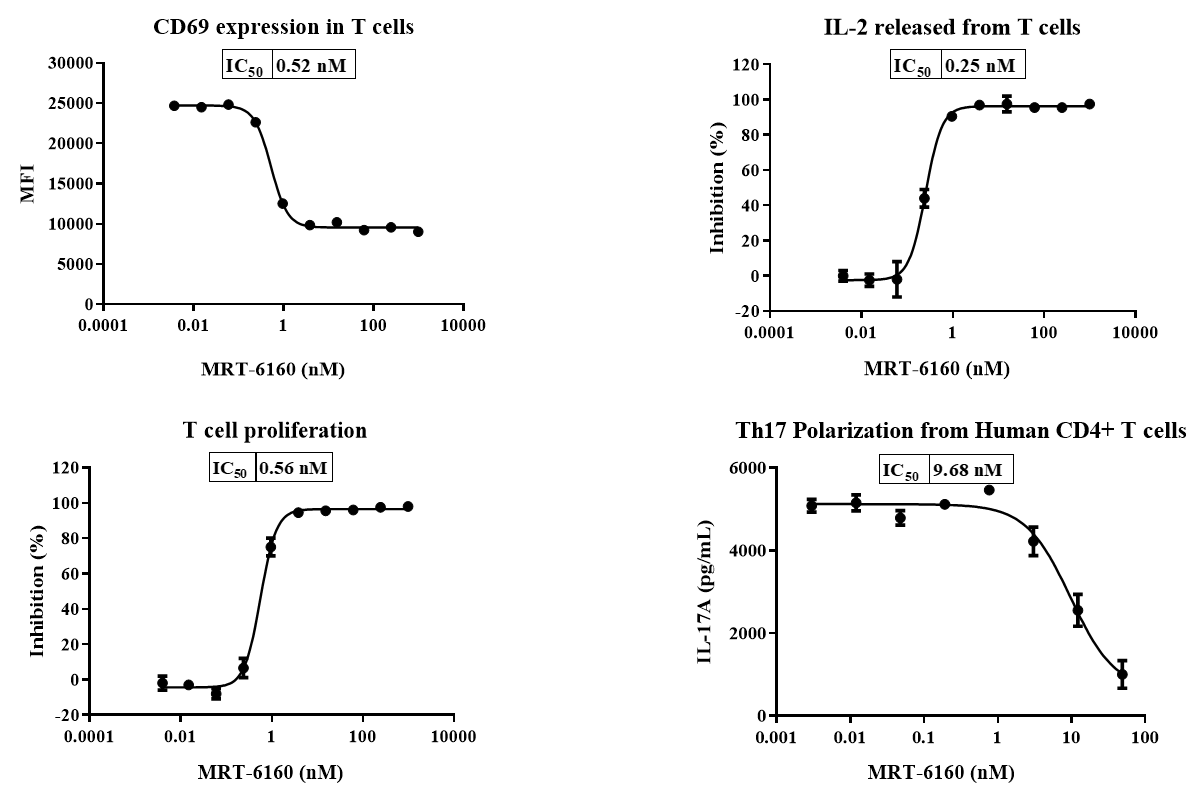
- Flow Cytometry: MRT-6160 significantly inhibited T cell CD69 expression and proliferation.
- ELISA: MRT-6160 significantly inhibited T cell IL-2 secretion and Th17 differentiation.
MRT-6160 Attenuates BCR-mediated Activity in Primary Human B Cells
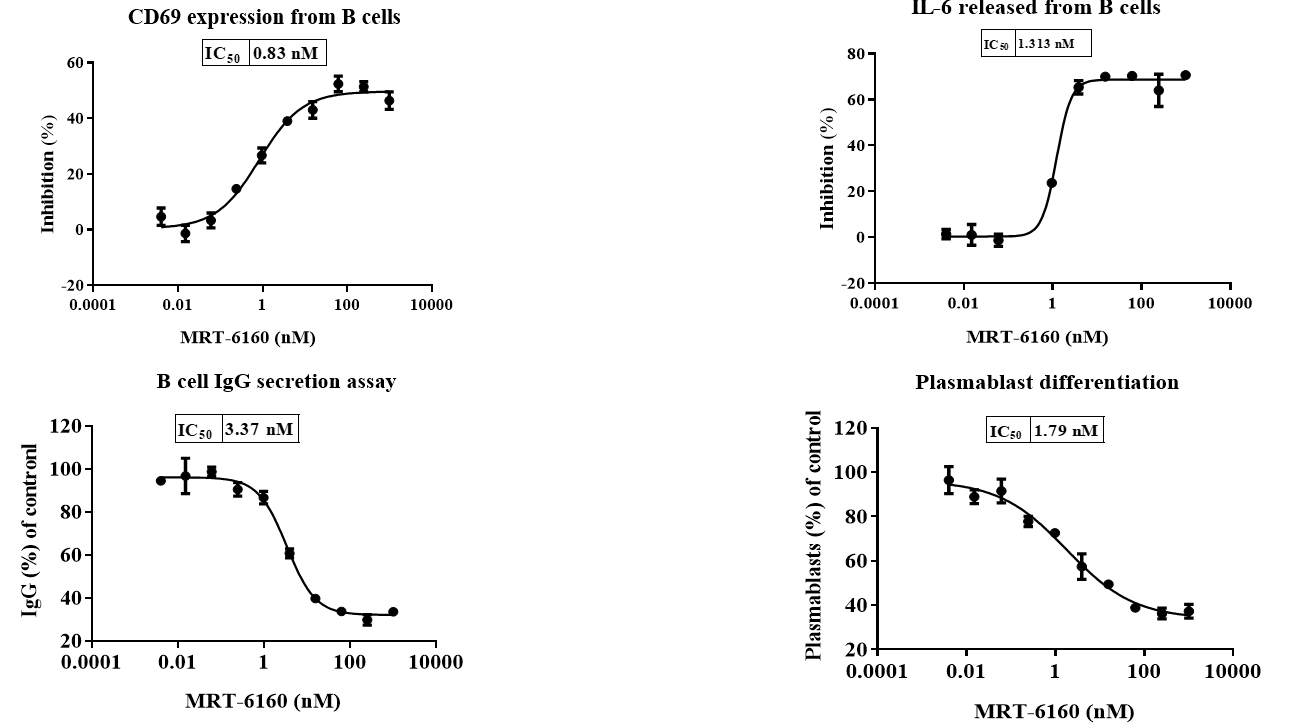
- Flow Cytometry: MRT-6160 significantly inhibited B cell CD69 expression and the proportion of plasmablast cells.
- ELISA: MRT-6160 significantly inhibited B cell IL-6 secretion and sIgG secretion.
VAV1 Degradation in Mouse PBMC & Spleen
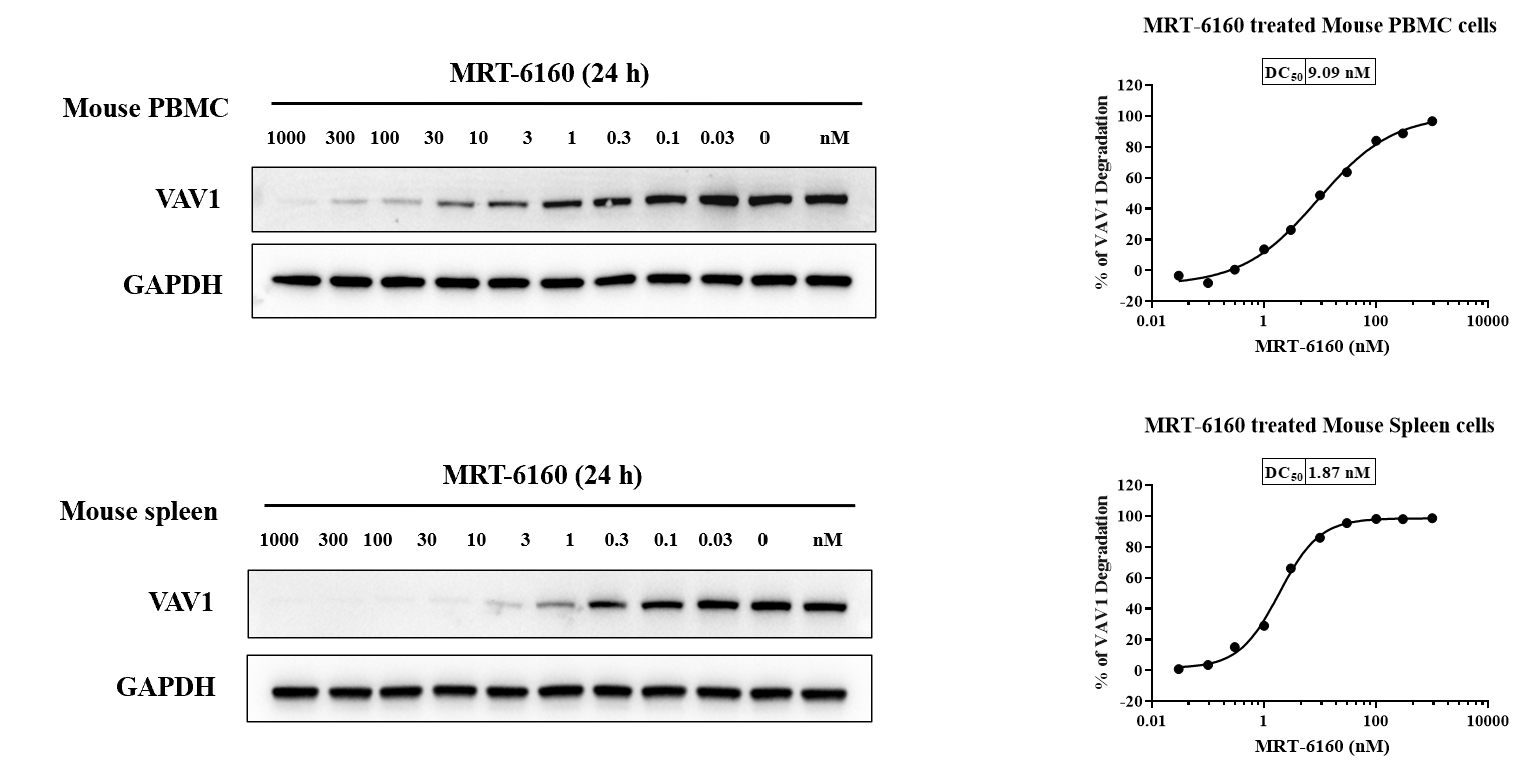
- Result: In mouse PBMC and spleen cells, MRT-6160 degraded the VAV1 protein with DC50 values of 9.09 nM and 1.87 nM, respectively.
- Predictive Value: This experiment can be used to predict the in vivo activity of VAV1 degraders.
- Western Blot: The slide includes Western blot images showing VAV1 and GAPDH levels at various concentrations of MRT-6160.
Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Spleen Tissue and PBMC Samples after MRT-6160 Administration in Mice
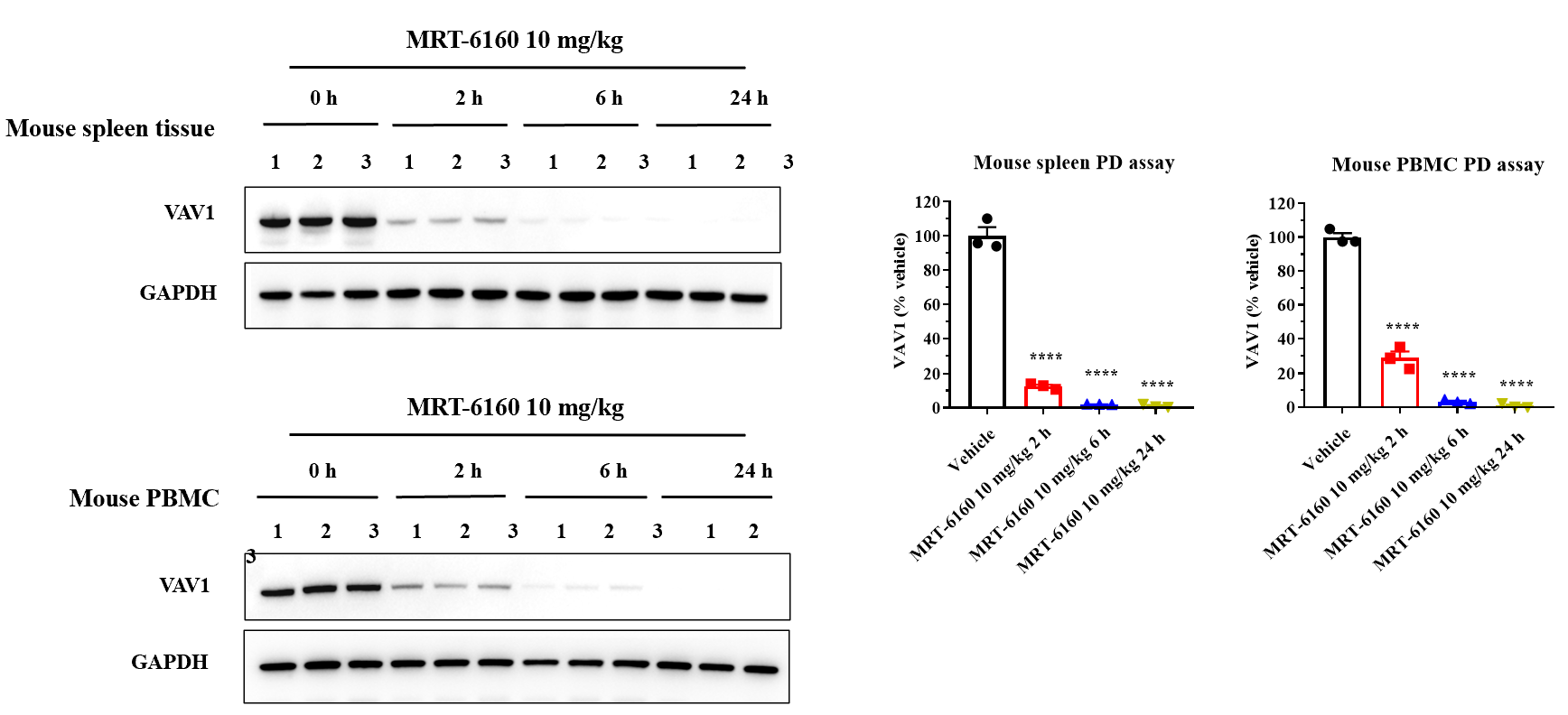
- Result: After a single dose of 10 mg/kg MRT-6160, Western blot results showed that the compound efficiently degraded VAV1 protein in mouse spleen and PBMC samples at different time points (0, 2, 6, and 24 hours).
Efficacy of MRT-6160 in EAE Model
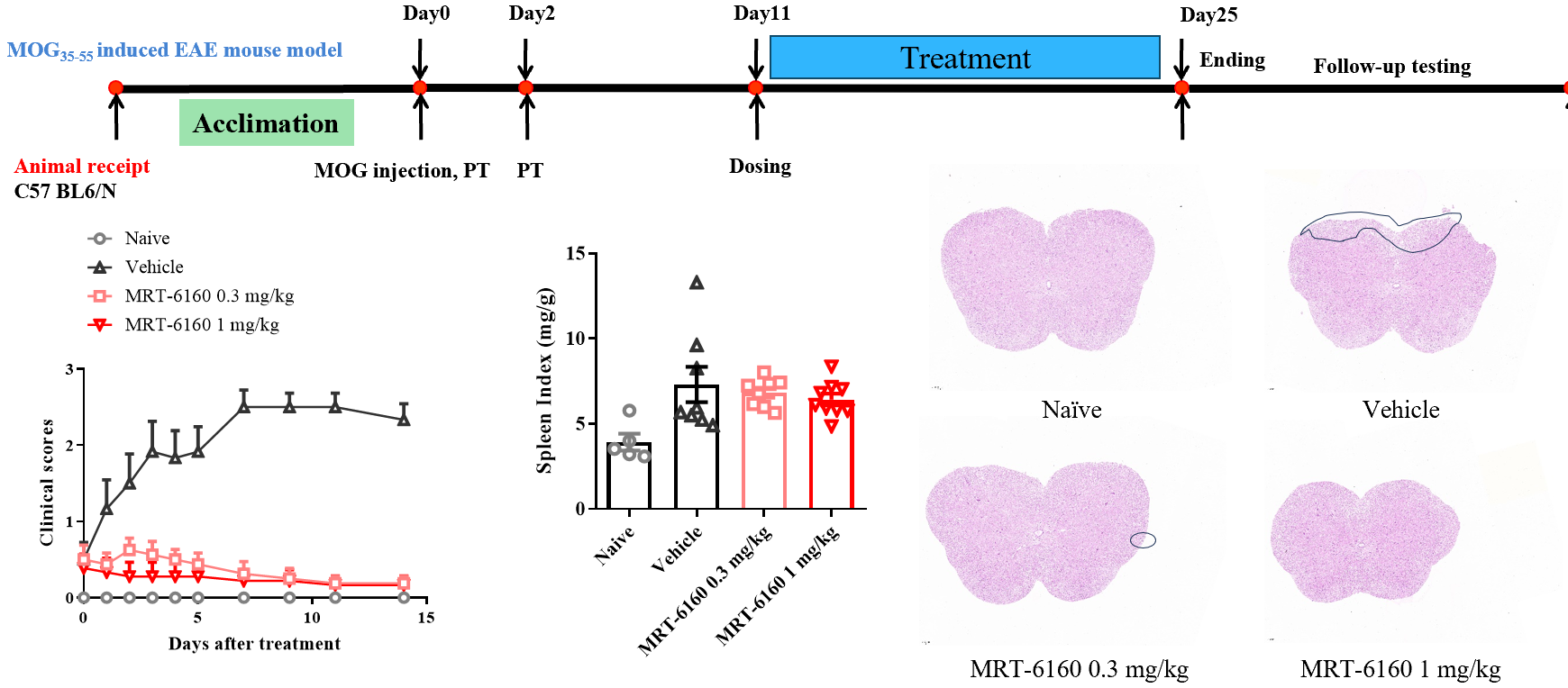
- Efficacy: In the MOG-induced EAE mouse model, therapeutic administration of MRT-6160 significantly inhibited disease progression, showing clear efficacy at a dose of 0.3 mg/kg.
- Splenomegaly: It did not show a clear inhibitory effect on EAE-induced splenomegaly.
- Histopathology: It significantly improved the reduction of spinal cord myelin protein and inflammatory cell infiltration.
- Animal: C57BL/6N.
- Protocol: The timeline shows the protocol starting with animal recepti
- on and acclimation, followed by MOG immunization and PT injection on Day 0 and Day 2. Dosing starts on Day 11 and continues until the experiment ends on Day 25.
Efficacy of MRT-6160 in Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Mouse Model
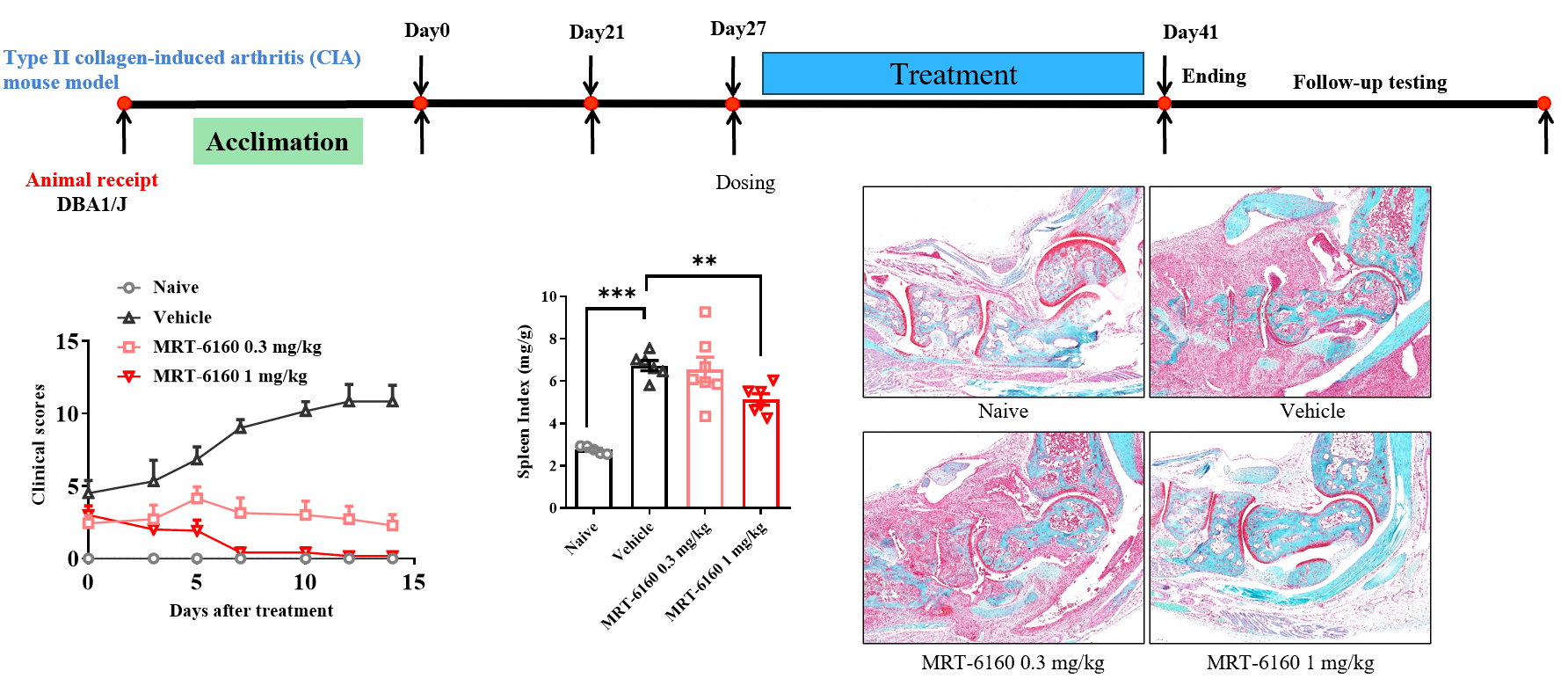
- Efficacy: MRT-6160 dose-dependently alleviated the symptoms of type II collagen-induced arthritis, showing a clear effect at 0.3 mg/kg.
- Splenomegaly: It also dose-dependently inhibited CIA-induced splenomegaly.
- Animal: DBA1/J.
- Protocol: The timeline shows the protocol starting with animal reception and acclimation, followed by the first immunization on Day 0 and the second on Day 21. Dosing starts on Day 27 and continues until the experiment ends on Day 41.
Efficacy of MRT-6160 in Adoptive Naïve CD4+ T cell-induced IBD Model
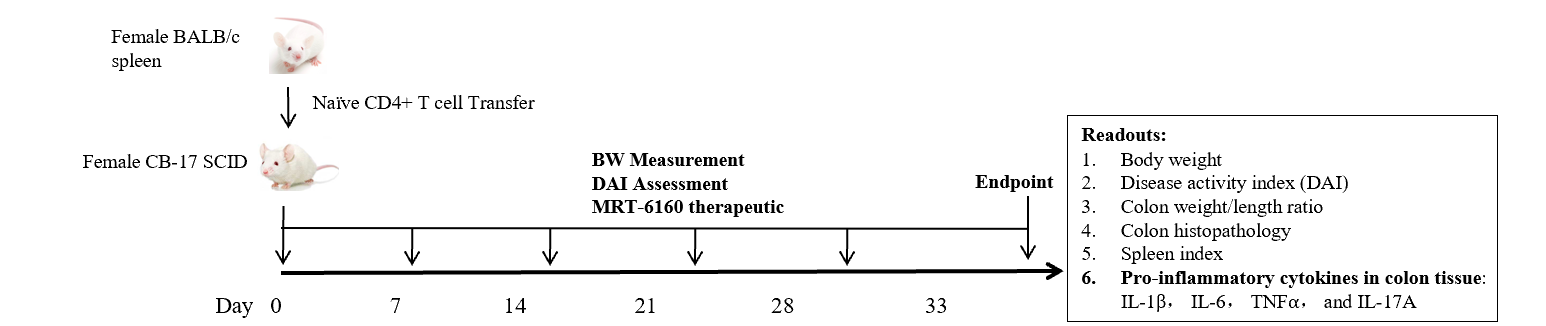
- Groups: Naïve, Vehicle, MRT-6160 (0.3 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg), and BMS-986165 (25 mg/kg).
- Dosing: The doses were administered orally (PO) once daily (QD) for 4-5 weeks, except for BMS-986165 which was given twice daily (BID).
- Readouts: The readouts for this study included body weight, Disease Activity Index (DAI), colon weight/length ratio, colon histopathology, spleen index, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in colon tissue (IL-1β, IL-6, TNFα, and IL-17A).
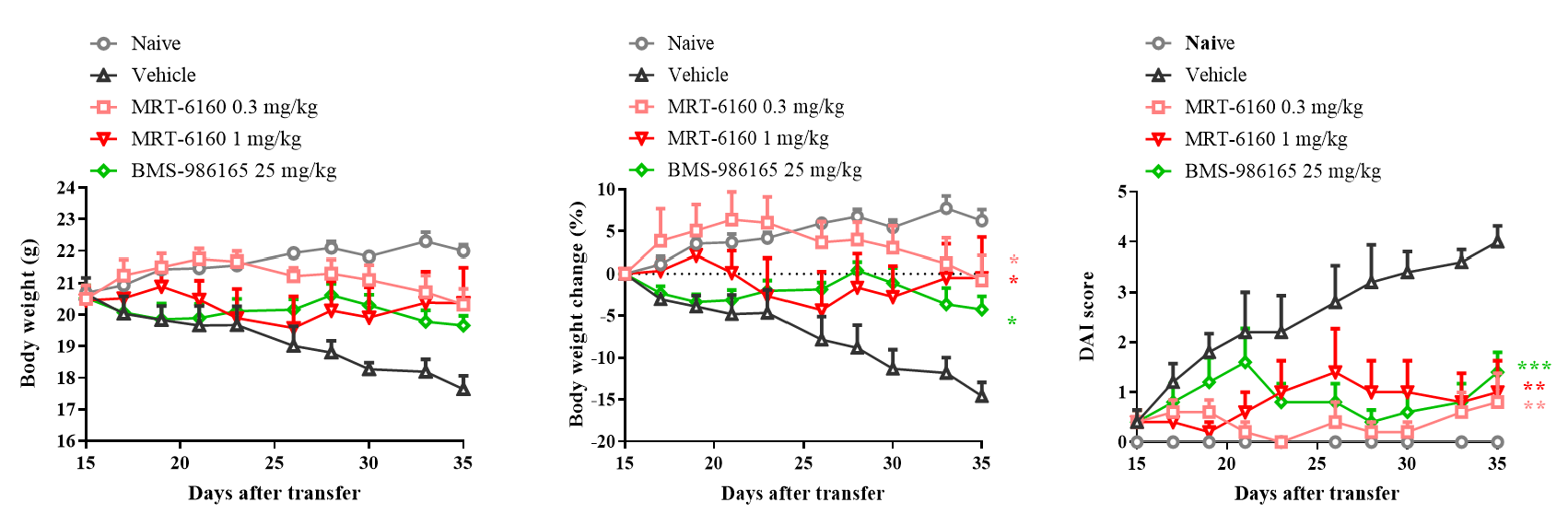
- Efficacy: In the IBD mouse model induced by adoptive transfer of Naïve CD4+ cells, therapeutic administration of MRT-6160 significantly inhibited disease progression, showing a clear effect at the 0.3 mg/kg dose.
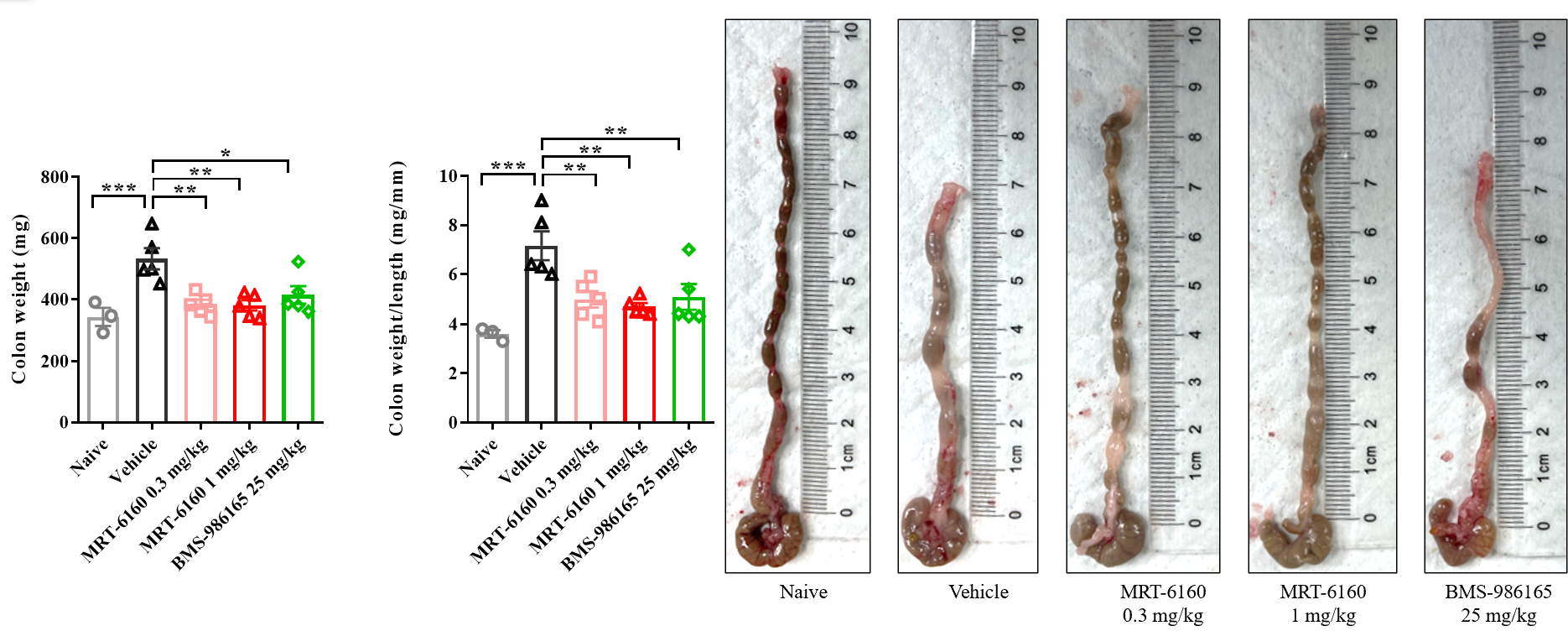
- Result: In the IBD mouse model, the colon becomes shorter and heavier. MRT-6160 was able to significantly improve the colon weight-to-length ratio, showing a clear effect at 0.3 mg/kg.
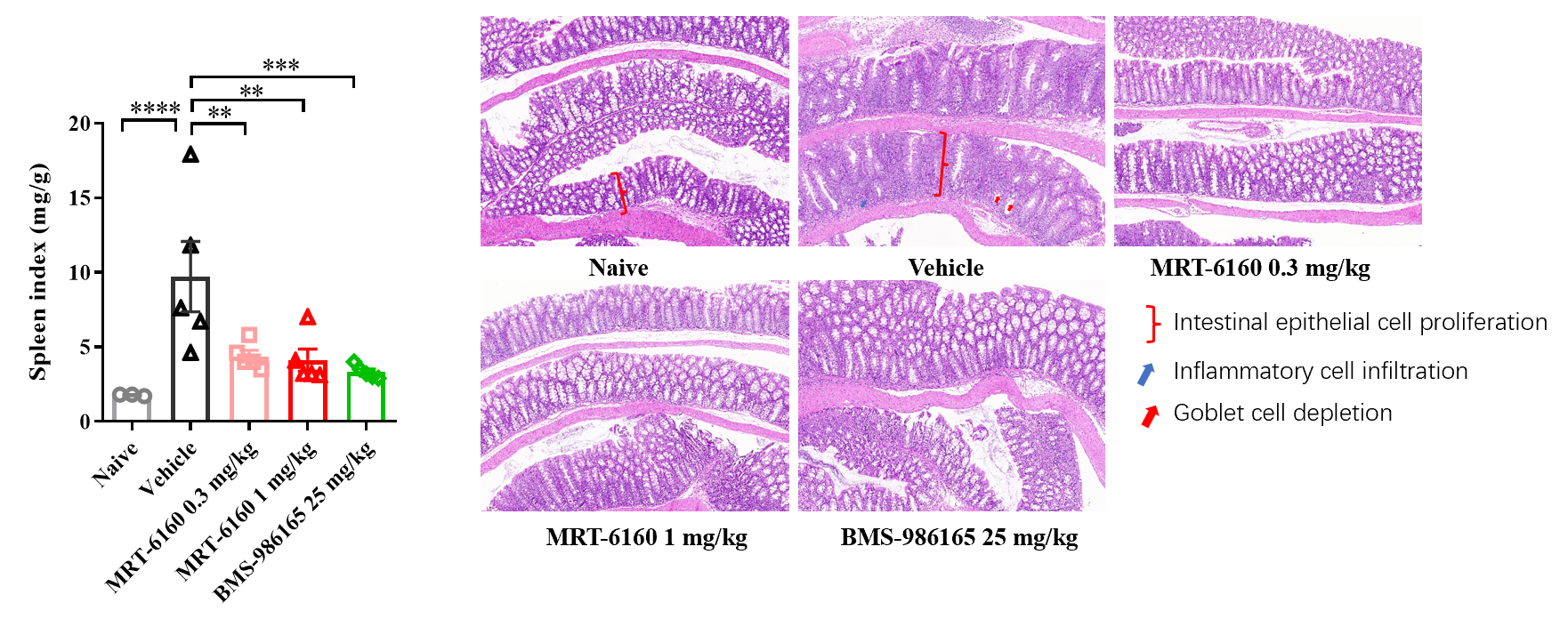
- Splenomegaly: In the IBD mouse model, MRT-6160 significantly inhibited splenomegaly, with a clear therapeutic effect at the 0.3 mg/kg dose.
- Histopathology: MRT-6160 also significantly improved colon pathological damage, including reducing inflammatory cell infiltration and increasing goblet cells.
Efficacy of MRT-6160 in Psoriasis Model
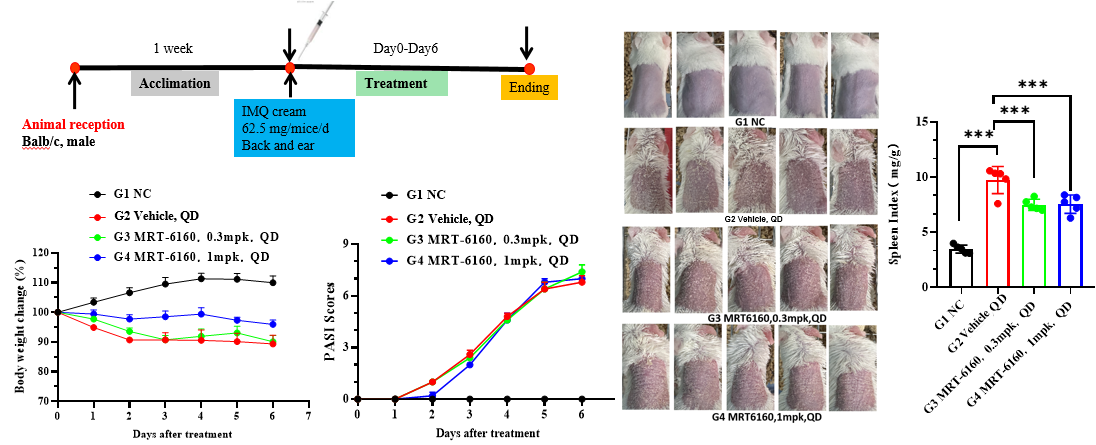
- Efficacy: In the Imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model, MRT-6160 did not show clear efficacy at 0.3 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg doses. Even at a higher dose of 10 mg/kg, it did not show clear efficacy.
- Splenomegaly: It did, however, significantly inhibit the splenomegaly caused by imiquimod.
- Protocol: The protocol section shows a 7-day treatment with 62.5 mg/mice/day of IMQ cream applied to the back and ear of Balb/c mice.
Conclusion
The molecular glue degrader, MRT-6160, is a potent and effective VAV1 degrader in both in vitro and in vivo models. Its robust activity in various immune-related disease models, including EAE, CIA, and IBD, highlights its potential as a therapeutic candidate for autoimmune and inflammatory conditions.
Recent information
